Learn more about forging foundries—find out the procedures, equipment, and trends that underlie current metalworking and manufacturing methods that are used in the field today.
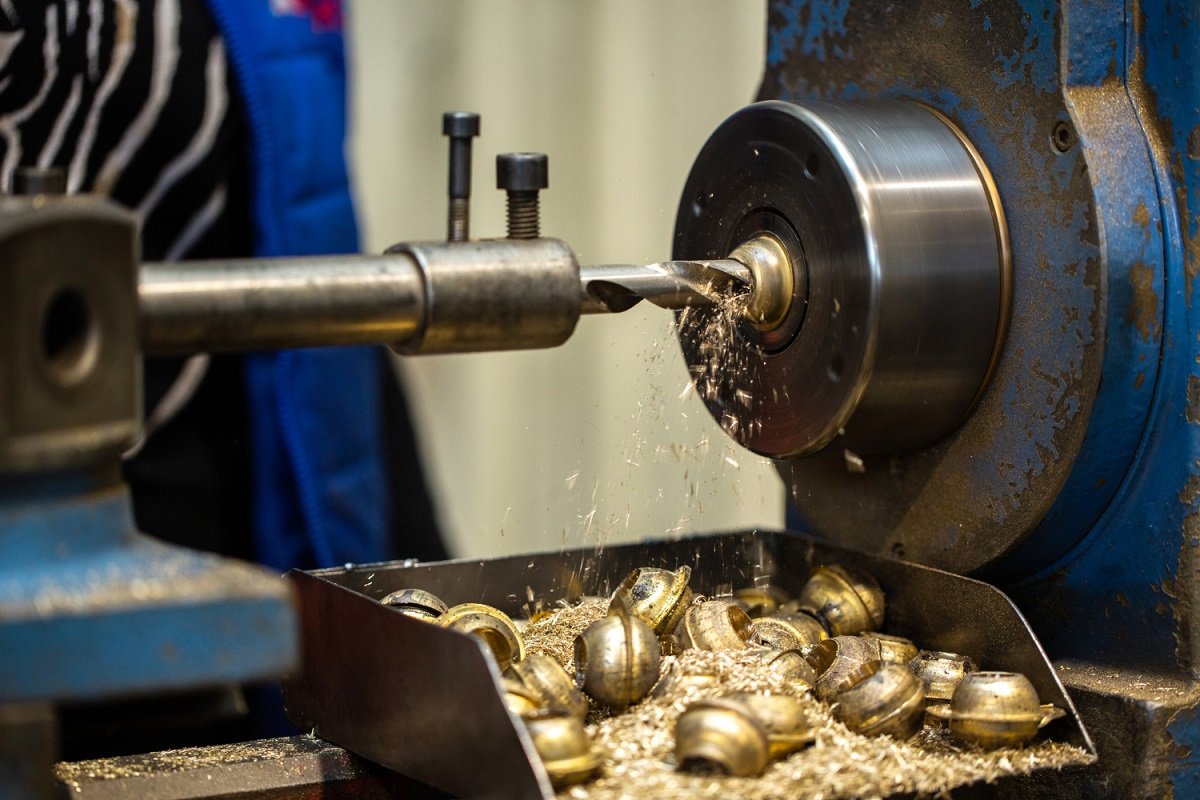
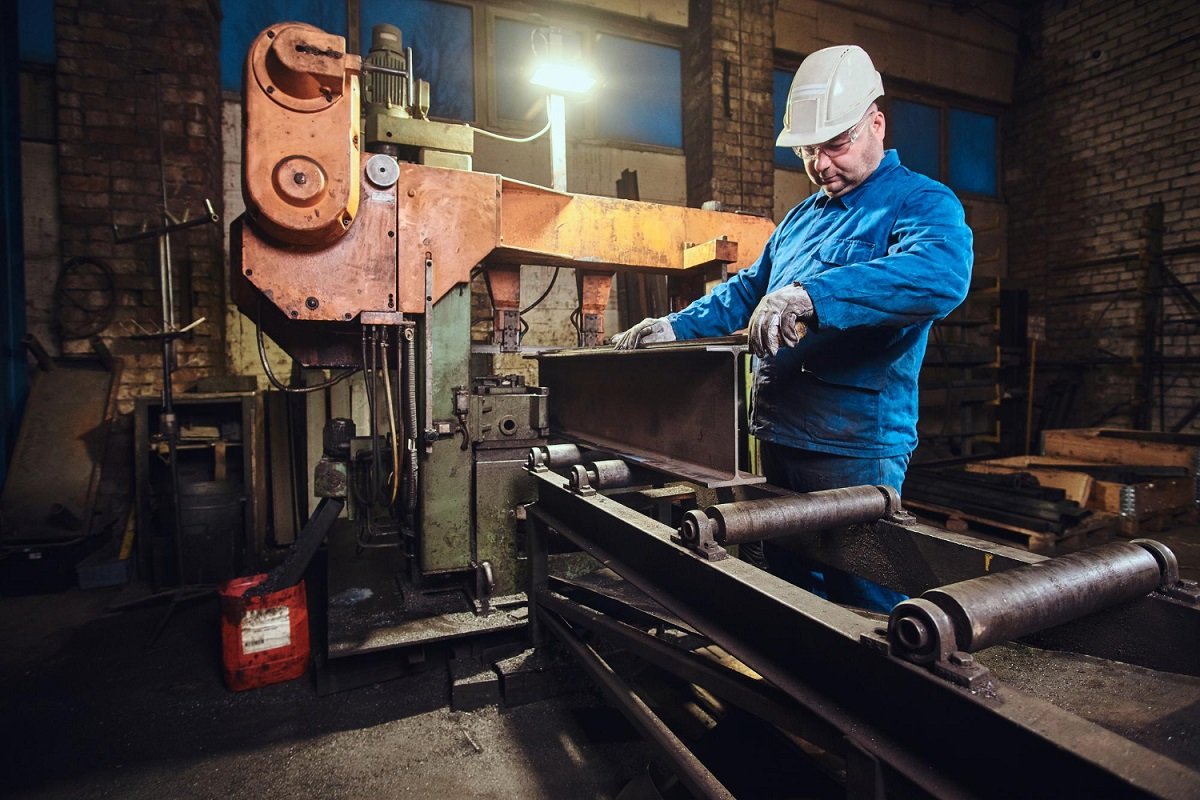
Forging foundry is basically a place where metallic tools are designed for specific purpose or use by heating to forge the metals, and they are then hammered or pressed with modern pressing machines or hydraulic presses to give the desired shape, structure, or design.
It combines the forging and foundry process. In simpler words, it is a forging foundry that is used to shape hot metals into required forms by pressure, mainly for tool parts and machinery parts or other related products.
How to ensure quality control in forging foundry?
Quality control in a forging foundry will involve several critical activities that will serve to maintain the quality integrity of its products. The first aspect is ensuring the quality of the raw materials used. As with the components, the foundation of a sound product relies on its component parts.

Testing and inspection of the raw materials will ensure defects and damage are identified early enough. To minimize defects, the forging process must include precise temperature control, repeated hammering or pressing, and design specifications.
Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic or radiographic testing, may also be utilized to establish the existence of internal defects within the forged parts without necessarily damaging them.
Competent manpower and regular machinery performance checks have an influence on retaining the accuracy and consistency of the final products.
It will, therefore, help trace all stages of the process, thus being a useful tool for developing critical areas of improvement. This leads to a strong quality control system.
Related: What is Pigments? How it Makes Your Paint Work!
Good manufacturing practices for forging foundry
GMP in any forging foundry mainly provides guarantees for product quality, safety, and efficiency of the production process. Some of the items include high-grade raw materials, precise temperature control in heating, and latest machinery for exact and repeatable forging.
Regular maintenance of equipment ensures optimum performance and strictly guideline-following workers minimize errors and waste. Non-destructive testing and inspection at different stages ensure early detection of defects.
The end product thus meets the quality standards. Documenting every step and maintaining traceability enable accountability and improvement in production efficiency.
Related: 7 Different Types of Asphalt Mixing Plants
Common techniques used in forging foundry
Some common techniques used in forging foundries include open-die, closed-die, and roll forging. Open-die forging is the process of shaping heated metal in between flat or contoured dies; however, the material does not completely get enclosed. This is usually done for large parts, fashioning simple shapes.
Closed-die forging is also known as impression-die forging; this method applies the use of dies to enclose the metal, thus permitting much more complex, precise shapes. Roll forging is that process by which the heated piece of metal is passed between two rollers to reduce its thickness and achieve a desired shape.
Other techniques include upset forging and press forging, where pressure or force, from different angles, is applied on other specific parts. Along with proper heating and cooling processes, these ensure that the metal acquires the required mechanical properties and shapes.
Related: Understanding Multicore Flexible Cable Manufacturing Processes
Different applications of forging foundry
Most of the components manufactured in forging foundries are widely applied in various industries. For example, in the automobile sector, crankshafts, gears, and connecting rods are considered the most critical forged parts because they make any vehicle robust and efficient.
In the aerospace industry, forging is applied to create lightweight, high-strength components such as landing gear, turbine blades, and structural members, as the forging process can endure extreme conditions.
Construction uses forged steel primarily for producing heavy-duty tools, railings, and support structures; the oil and gas industries use forged valves, fittings, and drilling equipment because of the strength and environmental resistance required.
Such examples of its applications include parts on medical devices as well as agricultural machinery, intended to be long-lasting and reliable.
Related: Things to look for while choosing wires and cables manufacturers in India
Limitation of forging foundry
While forging foundries are readily available and hold a myriad of benefits, the process does have several downsides. Major amongst these include a very expensive up-front cost in forging equipment and die manufacturing, which prevents it from being as economical with small production runs or even to carry out as a more custom order for low volume manufacturing.
Also, the complexity of forging processes can limit the ability to produce a certain number of intricate or highly detailed parts without additional machining or finishing. In addition to these drawbacks, forging costs are operational due to the critical need for temperature control.
The process also requires skilled labour. Where metal usage is concerned, the types of metals available are limited because not all can withstand such extreme conditions encountered when forging. Lastly, the forging process is highly energy-intensive and less environmentally friendly compared with some other manufacturing processes.
Related: Submersible Pump vs. Compressor Pump: Which One is Right for Your Needs?
What shall government do to encourage forging foundry in India?
The following are some strategic measures through which the government can encourage the growth of forging foundries in India.
First, financial incentives like subsidies, tax breaks, or low-interest loans can be offered to newly setup forging companies as well as to the existing ones, thus easing the financial burden and encouraging investment in advanced technologies and equipment.
Special economic zones (SEZs) for manufacturing can be opened up to encourage collaboration, smooth logistics, and access to resources. Training programs and skill development programs started with the support of technical institutes would ensure that skilled personnel could employ modern forging techniques.
Harmonious quality standards and certifications to support such steps would further enhance the reputation of Indian forging foundries in global markets.
At last, research and development in innovative forging techniques and materials would make it viable for the industry to remain sustainable and competitive, thereby contributing to the large manufacturing sector of India as well as to general economic growth.
In conclusion, forging foundries are considered one of the main players in the manufacturing world due to the fact that they are able to provide particular abilities for high-strength component production to support these different industries: the automotive and aerospace sectors, as well as construction.
It is possible to design an advanced technique in order to create a product with strict quality control, but so that final product would be reliable and would meet the demanding specification; however, and at various challenges, may not allow growth.
Government initiatives that are supportive of such forging foundries will be highly competitive in the forging environment to be established in India, thereby boosting the sector further.
Once such positive aids and practices are adopted, the forging sector can continue its good practices on its way to great contribution to the country’s manufacturing sectors and overall economic developments.
Related Posts: