In the realm of fluid management, strainers are very vital for preserving the lifetime and efficiency of pipe systems. The impurities in gases and liquids are filtered out so that a clean raw feed reaches critical devices such as pumps, valves, and heat exchangers. Strainers, as well as other pollution agents like trash and silt, keep away blockage and failure that would have jeopardized the entire system.
There are many kinds and designs for strainers; among the most often used are Y-type and T-type ones. Every kind has special qualities and advantages, catered to various uses and operational needs. Engineers, maintenance staff, and facility managers aiming at ideal flow management in their systems must first understand these variations.
One can’t emphasize the value of strainers any more. From food and beverage manufacture to water treatment and chemical processing, the presence of foreign particles may cause expensive downtime, equipment failure, and impaired product quality in sectors spanning from Investing in the correct kind of Y-type strainer manufacturer not only gives profits but also improves the operation of your system and increases the lifetime of your equipment, thereby saving a great amount of money over time.
How do Y strainers and T strainers differ in design and application?
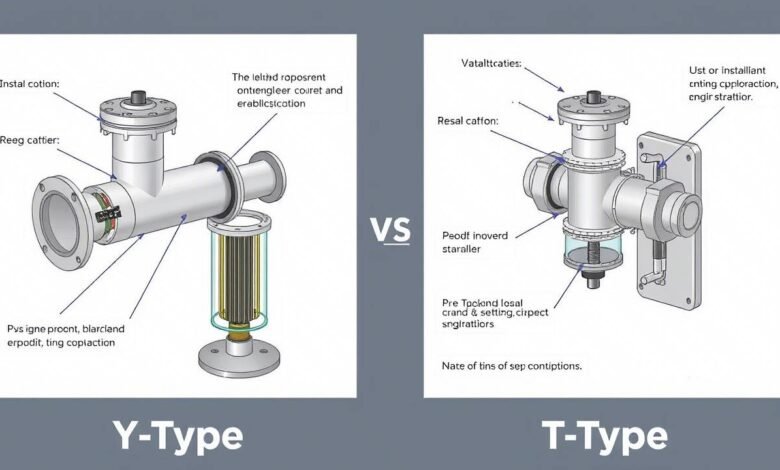
Strainers are essential components in pipe systems because they remove debris from the system to keep downstream components safe and functioning. Installable and maintainable are the strainers. Conversely, T strainers are better suited for heavy-duty uses and have less pressure drop. Concerned about the expenses, a Y-type strainer is a preferable choice as its housings are cast. Unlike a T-type strainer, which is somewhat costly, it is the ideal training option as it gives users flexibility.
Describe the major parts and purposes of a T and a Y strainer.
Y-strainers get their name from their Y-shaped construction. Their body contains a specifically made mesh screen to filter service fluids.
Custom manufactured T Type Strainers using conventional comparable T flanges or pipe plates Made of stainless-steel perforated sheet or wire mesh held by perforated sheet filter components For modest nominal bore straining needs, T Type Strainers are a reasonably priced fix.
To guarantee longevity and function, what materials are usually utilized in the building of T and Y strainers?
Variations in Body Materials Applied
The materials Y strainers are composed of help one to decide the kinds of situations and uses for which they are most appropriate. They find employment in steam, liquid, natural gas, and air pipelines, among other uses. The most often used Y strainer materials and advised uses are shown below.
1. Stainless Steel
Made of stainless steel, Applications where independence from contamination and resistance to high corrosion is needed usually call for y strainers. Food, chemical, and pharmaceutical sectors all find it to be their favourite medium. Still, stainless steel might be more costly than some of the other Y strainer materials available.
2. Cast Iron
Usually employed in pipe systems lacking high pressure and high temperatures and when the system is not subjected to strong thermal or mechanical stress, cast iron Y strainers are Most often used in strainer body is cast Iron. Along with a range of other product and process applications, it is used in larger-sized potable water lines and some non-potable water systems.
3. Carbon Steel
Robust carbon steel Y strainers are highly resistant to mechanical and thermal stress and utilized with great pressure and temperatures. Applications with a fire risk also find usage for them. Mostly the oil and petrochemical sector uses carbon steel bodies.
4. Bronze
Removing dirt, rust, and glue from pipe systems is easy by using bronze y strainers. Applications for brackish, saline, and saltwater, as well as for potable water services needed for bronze bodies and strainers. Still, it costs more than a few of the other choices.
5. Brass
A reasonably priced answer for many uses is brass and strainers. Upstream installations often use brass to guard control valves, pumps, and regulators against undesired substances such as pipe scale and rust.
FAQs:
What are the common failure modes of Y strainers and T strainers, and how can they be avoided?
The point where the screen or straining element seals to the body is another important consideration for Y-strainers. Careful machining of this seat will prevent particle bypassing. The screen should fit quite tightly. Watch out for strainers with non-machined seats. The wrongly positioned screen will enable bypass of the fluid letting dirt or trash downstream.
Bottom Line
Several Y-type strainer manufacturers are known for producing high-quality options made to order for many industries. In essence, one has to understand the differences between T-type and Y-type strainers. Making wise selections requires first thoroughly evaluating your operating requirements and the surroundings in which the strainer will be utilized.





